Why does toothache appear?
Toothache is not a coincidence or something that appears out of nowhere. It is usually due to an alteration inside the tooth or in the tissues surrounding it. The most frequent cause is caries which, when it advances without treatment, reaches the deepest layers of the tooth and irritates the dental nerve. When this happens, the sensitivity becomes a constant throbbing pain.
Another common cause is inflammation of the gums. Diseased gums can recede and expose the root of the tooth, an area that is very sensitive to cold, heat and pressure. In more advanced stages, gum infection can affect the supporting bone, intensifying the pain.
Wisdom teeth are also common protagonists of this type of discomfort. When they do not have enough space to erupt, they are partially covered by the gum and become easily inflamed, causing pain, local inflammation and even difficulty in opening the mouth.
>>> Do you live in Mallorca? Book your free first appointment <<<
In other cases, the pain appears after a dental fracture, either due to a blow or severe wear, which exposes the internal tissue. Even habits such as grinding the teeth at night (bruxism) can cause microcracks and overload on the teeth, causing a diffuse pain that is confused with other pathologies.
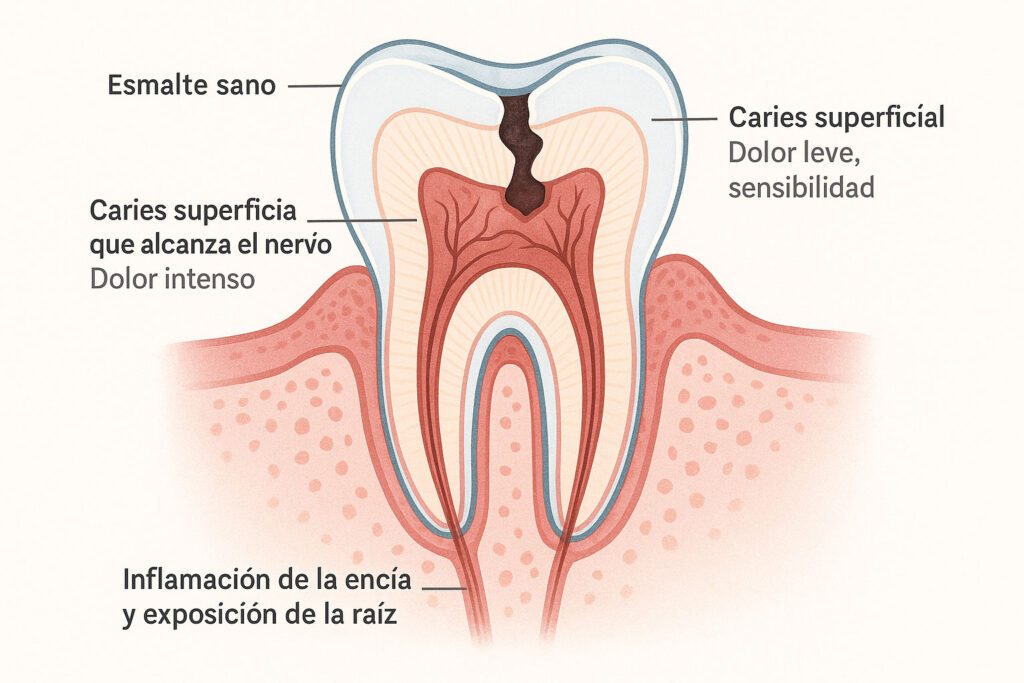
How to identify if the toothache is severe
Not all toothaches have the same intensity or the same origin, and it is essential that you know how to distinguish when it is a temporary discomfort and when we are facing a problem that requires immediate attention.
A mild toothache usually manifests itself as a sensitivity to cold, heat or sweet foods. In these cases, the toothache appears only during the stimulus and disappears afterwards. This type of discomfort is usually due to a superficial cavity or slightly inflamed gums.
On the other hand, when the toothache becomes constant, stabbing and does not subside with common analgesics, we are talking about an intense pain that may indicate a deep infection or advanced damage of the dental nerve. If there is also swelling of the face, difficulty in opening the mouth, fever or general malaise, these are warning signs that should not be ignored.
To help you better visualize these differences, here is a simple comparison table:
Mild toothache | Severe (severe) toothache |
Sensitivity to cold, heat or sweets. | Constant stabbing pain that does not go away. |
It calms down when the stimulus is removed. | It does not improve with common analgesics. |
Located in a single tooth. | It may radiate to the ear, jaw or head. |
There is no visible swelling. | Swelling of gums, face or neck. |
No fever or general malaise | It may be accompanied by fever, malaise or tiredness. |
This type of distinction is important because mild pain can wait for a scheduled dental check-up, while severe pain, accompanied by inflammation or fever, requires urgent dental care to avoid complications.
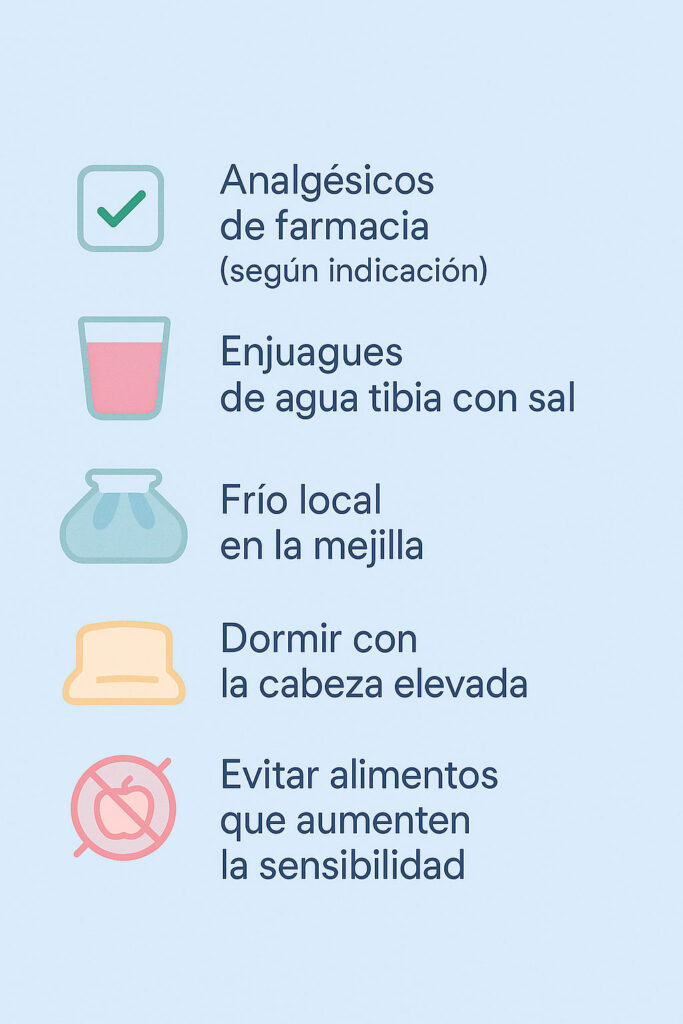
Temporary remedies until visiting the dentist
When toothache appears, the most important thing to remember is that no home remedy will solve the root of the problem. All we can do is alleviate the discomfort until the dentist can see you. Even so, these remedies can make the difference between an endless night and getting a better night’s rest.
Pharmacy analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs
The first option is to go to an on-call pharmacy. There you will find commonly used pain medications, such as paracetamol or ibuprofen, always following the instructions on the package insert and without exceeding the recommended doses. These drugs reduce inflammation and soothe the sensation of pain.
Rinses with warm water and salt
A very simple solution is to dissolve half a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water and rinse gently. This helps to cleanse the area, reduce inflammation and temporarily reduce pain.
Local cold on the cheek
Applying an ice pack wrapped in a cloth to the cheek at 10 to 15 minute intervals may reduce swelling and soothe the pain. It is essential not to apply heat, as this may worsen the infection if present.
Sleeping with the head incorporated
When we lie down, pressure increases in the affected area and pain often intensifies. Sleeping with the head slightly elevated, using an extra pillow, can help reduce this pressure.
Avoid certain foods
As far as possible, very sweet, cold or hot foods should be avoided, as they can trigger pain in an already sensitized tooth.
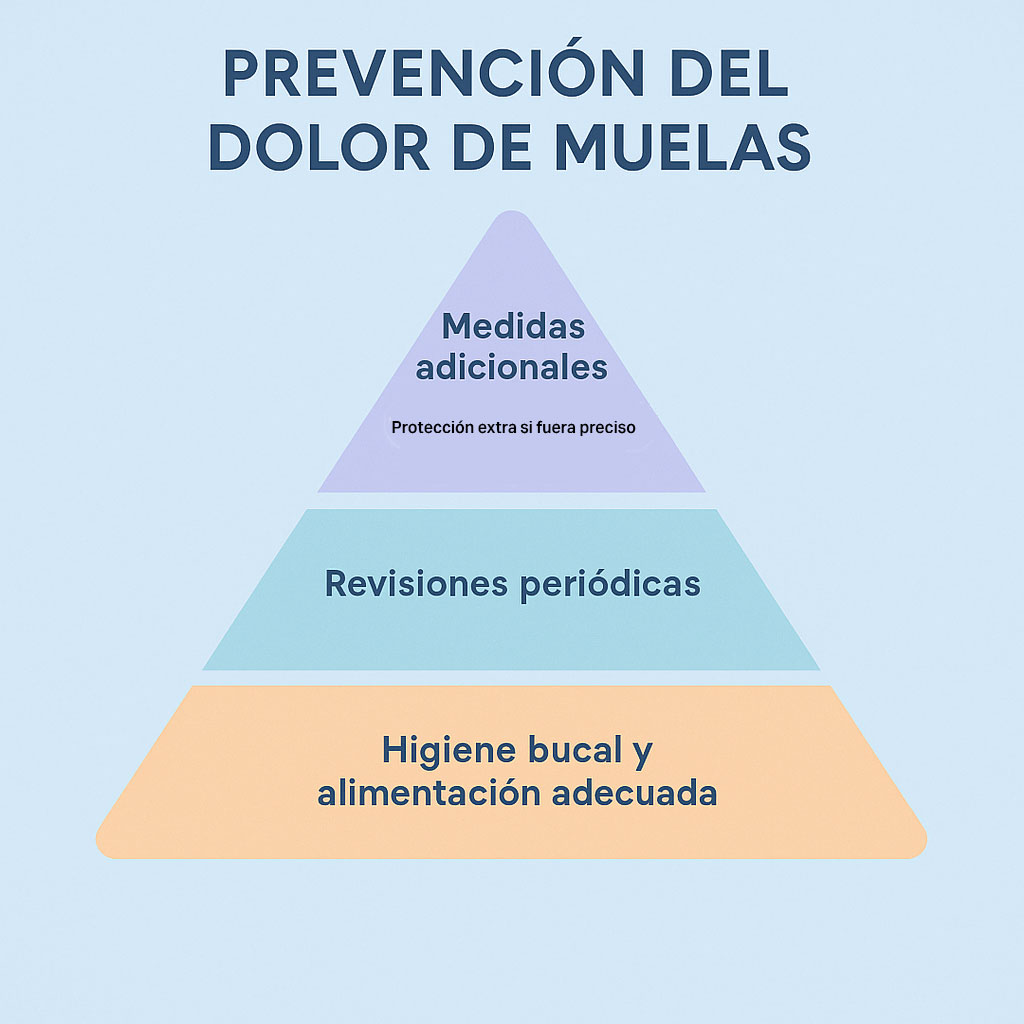
Prevention of toothache
The best remedy against toothache is to prevent it from appearing. Although it is not always possible, most cases of toothache are related to factors that we can control through simple habits.
Daily oral hygiene
Brushing your teeth at least twice a day, flossing and supplementing with mouthwash helps to remove food debris and plaque, which can otherwise lead to tooth decay and gum disease.
Periodic checkups
Visiting the dentist twice a year allows detecting incipient problems before they cause pain. A superficial cavity, treated in time, avoids the need for more complex treatments such as root canals.
Balanced diet
Reducing the consumption of sugars, carbonated beverages and highly acidic foods protects tooth enamel and reduces the risk of tooth decay. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables and dairy products provides minerals and vitamins that strengthen teeth and gums.
Beware of harmful habits
Smoking not only damages the gums, it also decreases healing capacity and increases the risk of infections. Similarly, bruxism (teeth grinding) can cause microfractures and pain, so it is advisable to consult a dentist if you suspect this habit.
Extra protection in special situations
In people with a high predisposition to caries, the dentist may recommend topical fluoride or sealants on the molars, especially in children and adolescents.
To make prevention more visual and easier to remember, we can represent it in a toothache prevention pyramid:
- Base of the pyramid (daily habits): constant oral hygiene and proper nutrition.
- Intermediate level: periodic check-ups with the dentist.
- Higher level: additional measures such as the use of unloading splints for bruxism or fluoride applications on a case-by-case basis.
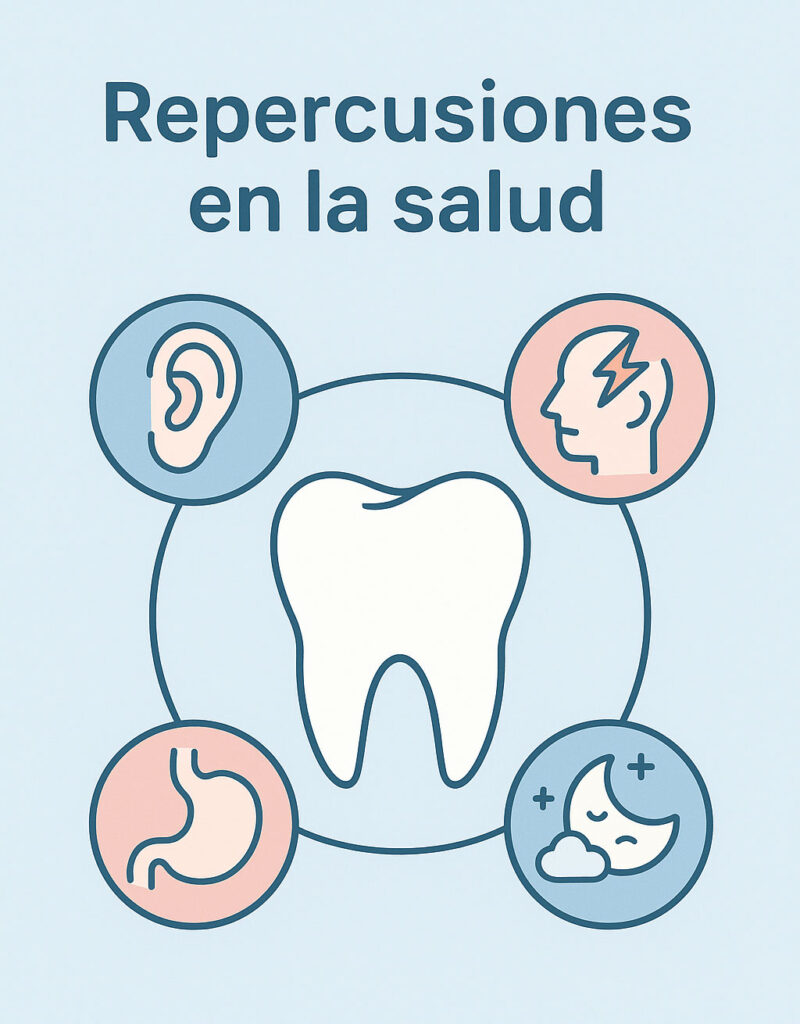
Impact on general health
Toothache does not only affect the mouth. When a dental problem remains untreated, it can trigger consequences in other areas of health that we often overlook.
Pain radiating to other areas
The dental nerve shares connections with other nerves in the face and head. Therefore, an infection or inflammation in a tooth can be felt as pain in the ear, in the jaw and even as a headache. In some cases, patients may mistake an affected tooth for otitis or temporomandibular joint problems.
Digestive problems
When pain is intense, we tend to chew worse or avoid certain foods. This can affect digestion and cause gastric discomfort, as the food does not reach the stomach well crushed.
Impact on rest and mood
Dental pain often intensifies at night, disrupting sleep and leading to daytime fatigue. In the long run, lack of rest and constant discomfort can affect work performance and mood.
Risk of more serious infections
An untreated dental infection can spread to nearby tissues such as bone, skin or sinuses. In more severe cases, the infection can reach the bloodstream and become a serious health problem.
Relationship with systemic diseases
Several studies have shown that chronic gum infections are related to increased risk of cardiovascular disease, decompensation in diabetic patients and complications in people with low defenses.
When to seek emergency care
Not every toothache requires immediate attention, but there are situations where it is not a good idea to wait. Ignoring symptoms can allow an infection to progress and become a bigger problem.
Warning signs that require urgent attention
- Intense pain that does not improve with common analgesics.
- Visible swelling of the gum, face or neck.
- Fever or general feeling of malaise.
- Difficulty opening the mouth or swallowing.
- Pain radiating to the ear, jaw or head.
In any of these cases, it is best to see a dentist immediately. If the pain appears at night or during a holiday, it is best to go to an on-call pharmacy to obtain temporary medication to help control the pain until the dentist can see you.
Why we should not postpone the visit
Dental pain is always a warning that something is wrong. If we let it advance, a simple cavity can turn into a more serious infection that affects the nerve, the bone or even spreads to other areas. The sooner action is taken, the simpler and faster the treatment will be, with fewer complications and less cost.

Summary of the article
Toothache should never be considered a simple passing discomfort. It is always a warning that something is happening inside the mouth: an advancing cavity, an inflamed gum, a dental fracture or even an infection. We can rely on temporary measures to cope with the situation -analgesics, rinses, local cold or a proper sleeping posture-, but these solutions are not a substitute for professional assessment.
Prevention remains the key. With rigorous oral hygiene, regular check-ups and proper nutrition, most dental pain can be avoided. In addition, we must remember that oral health is closely related to general health: an untreated dental infection can affect the ears, rest, digestion and even increase the risk of more serious diseases.
Therefore, the main message is clear: don’t ignore toothache. The sooner you go to your dentist, the simpler and faster the treatment will be, with fewer complications and greater peace of mind for your health.
 Whatsapp
Whatsapp


