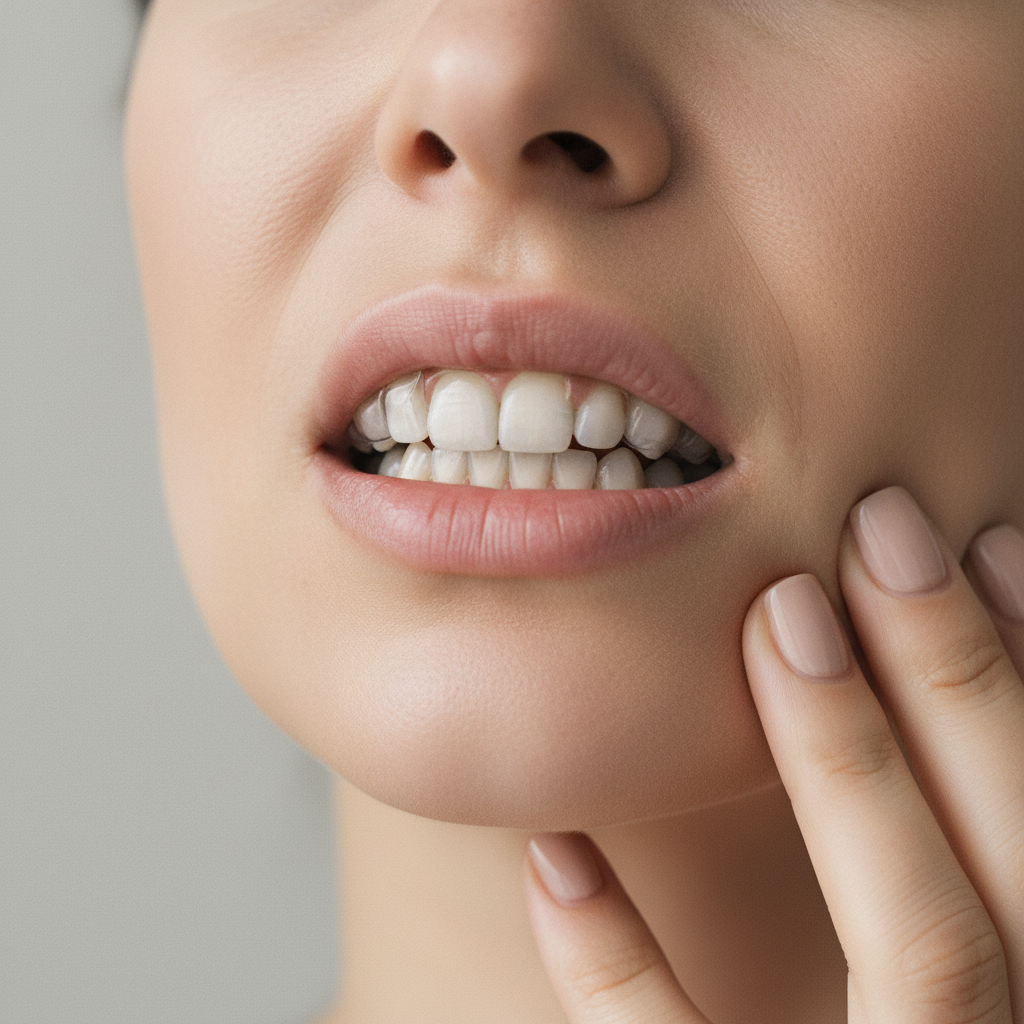
Swollen gums are one of the most frequent signs that something is wrong with your oral health. They are often accompanied by redness, sensitivity or bleeding when brushing, and although at first they may seem like a minor annoyance, they always indicate the presence of a problem that should be addressed.
This symptom can be due to common causes such as plaque build-up or poor hygiene, but also to more complex factors such as hormonal changes, smoking or even general diseases. The important thing to understand is that swollen gums should never be considered normal: they are a warning sent by the body.
While an appointment with the dentist is being made, there are simple measures that help alleviate the discomfort and stop the irritation. In addition, with good preventive habits, it is possible to reduce the risk of this situation recurring.
>>> Do you live in Mallorca? Book your free first appointment <<<
In this article we will explain why gums become inflamed, how you can relieve the discomfort at home and what preventive measures you should incorporate to keep your mouth healthy. You will also see the warning signs that require an urgent visit to the dentist to avoid complications.
Why do gums become inflamed?
Inflamed gums appear when the tissue surrounding the teeth reacts to an aggression, generally caused by bacteria. The most frequent cause is the accumulation of bacterial plaque: a sticky film formed by food debris and microorganisms that, if not removed daily with a good brushing, hardens into tartar. This irritates the gum, which responds with redness, inflammation and bleeding.
The first stage of this process is known as gingivitis, a reversible phase if treated in time. However, if left to evolve, it can develop into periodontitis, a more serious disease that affects the bone supporting the tooth and can lead to its loss.
However, plaque and tartar are not the only culprits. There are other factors that promote gum inflammation:
- Hormonal changes: pregnancy, adolescence or menopause may increase gingival sensitivity.
- Tobacco: decreases the blood supply to the gums and hides the signs of inflammation, causing the problem to progress silently.
- Medications: some drugs, such as certain antihypertensives or anticonvulsants, can cause abnormal gum growth.
- Nutritional deficiencies: lack of vitamins, especially vitamin C, can aggravate inflammation.
- Stress and systemic diseases: conditions such as poorly controlled diabetes also influence gingival health.
To better illustrate this difference, we can accompany this section with a simple comparative graph between healthy gingiva and inflamed gingiva:
- Healthy gingiva: pink color, firm, adapts well to the tooth and does not bleed when brushing.
- Inflamed gums: intense red color, increased volume, sensitivity, easy bleeding and even bad breath.
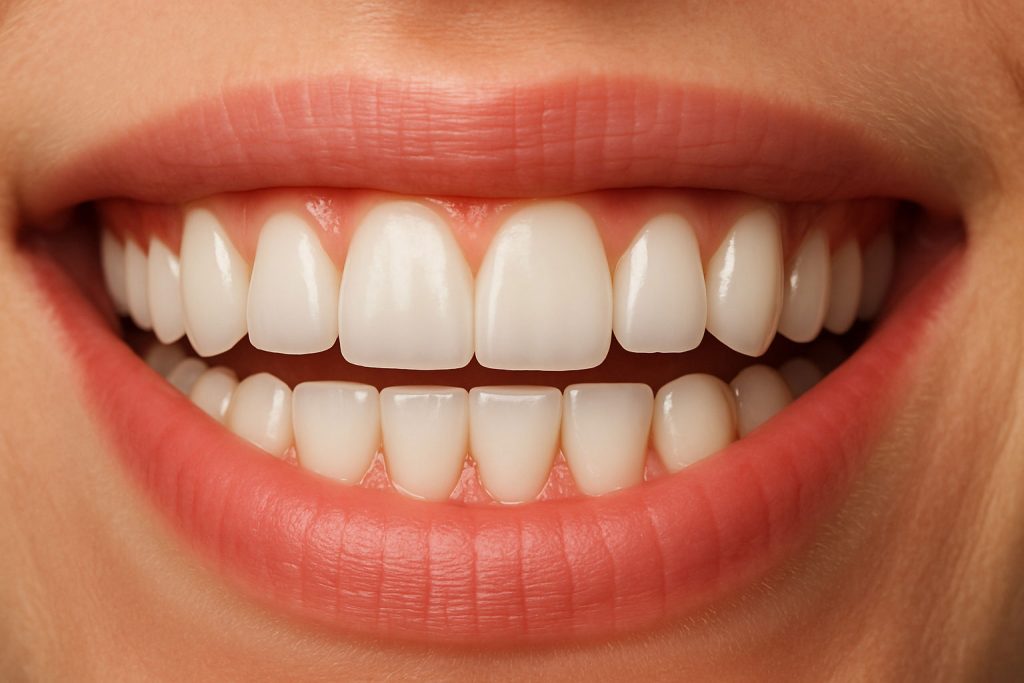

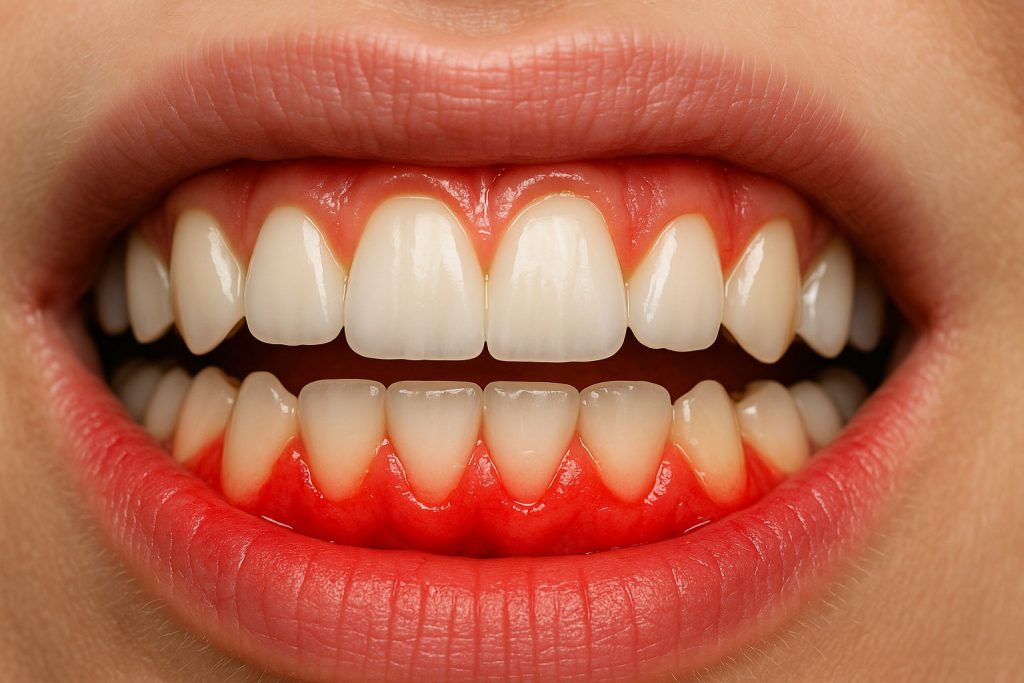
Gingivitis: the first warning sign of gum disease
Gingivitis is the initial stage of gum disease and the most common cause of gingival inflammation. It occurs when bacterial plaque accumulates at the line between the tooth and the gum, irritating the soft tissue.
At this stage, the most common symptoms are:
- Red and sensitive gums.
- Localized or generalized swelling.
- Bleeding when brushing or flossing.
- Persistent bad breath.
The important thing is that gingivitis is reversible: with proper oral hygiene and professional cleaning in the dental office, the gums can recover their healthy state without sequelae. However, if ignored, the problem can progress to periodontitis, where the bone supporting the tooth is already affected, compromising its stability.
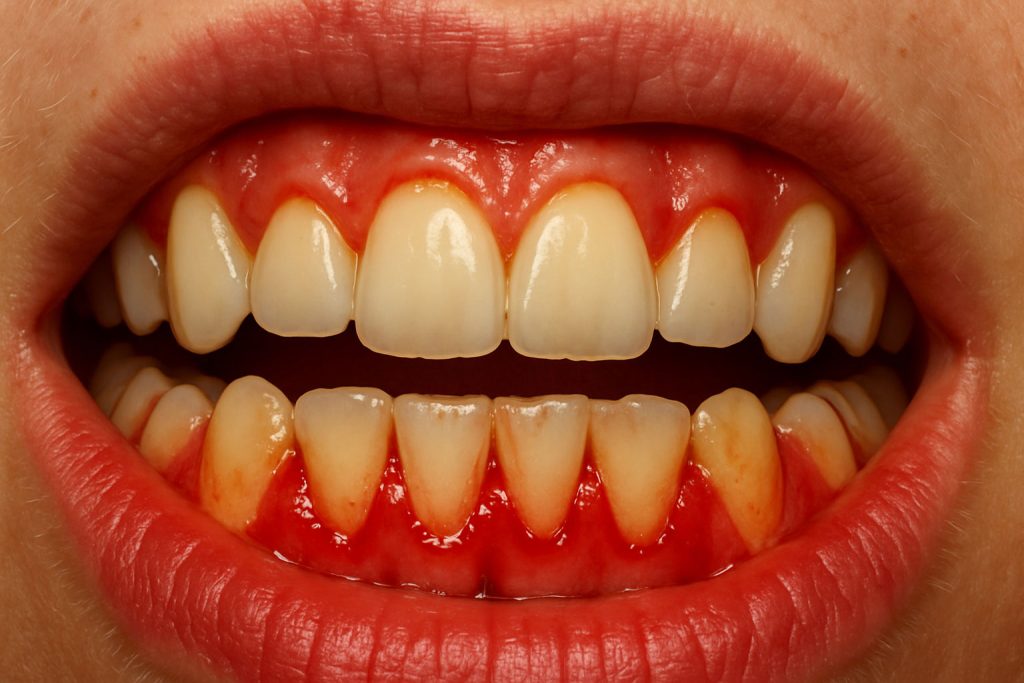
Periodontitis: when the inflammation progresses
Periodontitis is a more serious disease than gingivitis and occurs when gum inflammation progresses and begins to affect the supporting tissues of the tooth, including the bone. Unlike gingivitis, it is no longer reversible, although it can be controlled with specialized treatment to prevent its progression.
In periodontitis, the gum pulls away from the tooth forming periodontal pockets, where bacteria and tartar accumulate. Over time, these pockets deepen, the bone is destroyed and the teeth may begin to move.
The most common symptoms are:
- Swollen gums with spontaneous bleeding.
- Chronic bad breath.
- Retraction of gums that exposes the root of the tooth.
- Tooth mobility or the sensation of teeth “shifting”.
- In advanced stages, loss of teeth.
In addition, several studies have shown that periodontitis not only affects the mouth: it is related to systemic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular problems or premature births.
👉 To reinforce this point, we can plot a simple comparative graph:
- Gingivitis (superficial inflammation, reversible).
- Periodontitis (deep inflammation with bone loss and tooth mobility).
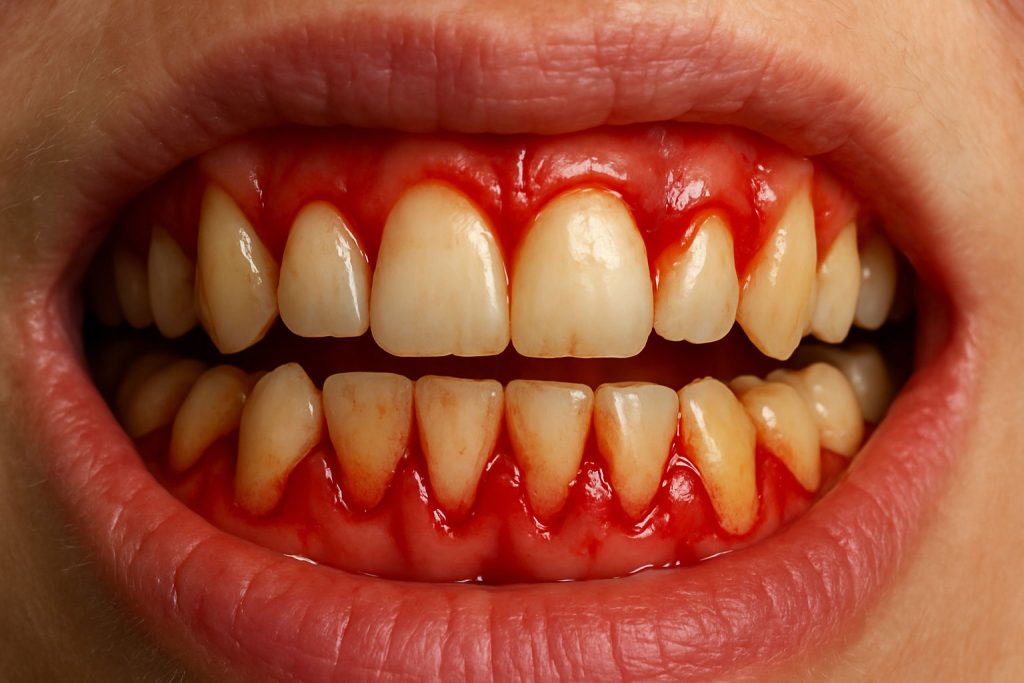
Symptoms of swollen gums: how to recognize their severity
Swollen gums do not always cause severe pain, so many people tend to ignore them. However, recognizing the symptoms early is essential to differentiate between a mild situation and a problem that requires immediate attention.
Mild symptoms
- Reddened and sensitive gums.
- Occasional bleeding when brushing or flossing.
- Slight localized swelling in some area of the mouth.
- Discomfort when eating very hard or hot foods.
Severe symptoms
- Spontaneous bleeding, even without brushing.
- Generalized inflammation and constant pain.
- Gingival recession (the gums appear to “pull down” and expose part of the root).
- Persistent bad breath, difficult to disguise.
- Mobility of the teeth or the sensation that they change position.
- Swelling that spreads to the face or neck.
Mild symptoms of swollen gums | Severe symptoms of swollen gums |
Redness and slight sensitivity | Frequent spontaneous bleeding |
Occasional bleeding when brushing | Constant pain and very swollen gums |
Mild swelling in specific areas | Gingival shrinkage and root exposure |
Discomfort when eating hard/hot foods | Chronic bad breath and tooth mobility |
– | Swelling affecting face or neck |
Temporary remedies to relieve swollen gums at home
When swollen gums appear, the most important thing is to visit the dentist to identify the cause and apply the appropriate treatment. However, while you wait for the appointment, there are measures that can help relieve discomfort and reduce irritation temporarily.
Warm water and salt rinses
Dissolving half a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water and gently rinsing can help reduce inflammation and keep the area cleaner, reducing bacterial growth.
Gentle brushing with a soft brush
Although bleeding can be scary, we should not stop brushing. It is advisable to use a soft bristle brush and make delicate movements to remove plaque without irritating the gums.
Mouthwashes with antiseptic
The use of chlorhexidine rinses can help control bacterial proliferation. However, they should only be used for short periods of time and under the indication of the dentist, since prolonged use may stain the teeth.
Commonly used analgesics
If the discomfort is significant, regular pharmacy analgesics can be taken, always following the recommendations on the package insert and without exceeding the doses.
Avoid irritants
During this time it is advisable to reduce or eliminate the consumption of tobacco, alcohol, very spicy foods, hard or with extreme temperatures, as they aggravate inflammation and increase pain.
How to prevent swollen gums
The best way to avoid inflamed gums is to adopt daily habits that keep the mouth in balance and to visit the dentist periodically to detect any problems early. Prevention is simpler and less expensive than treating advanced periodontal disease.
Complete oral hygiene
Brushing at least twice a day with proper technique is essential. Brushing should be complemented with dental floss or interdental brushes, which remove plaque in areas where the conventional toothbrush cannot reach.
Regular check-ups and professional cleanings
Visiting the dentist once or twice a year allows you to identify incipient inflammation and remove tartar that cannot be removed at home. These professional cleanings are key to maintaining long-term gingival health.
Balanced diet
A diet rich in fruits and vegetables, especially those with a high vitamin C and D content, helps to strengthen the gums. Conversely, it is advisable to moderate the consumption of sugars, carbonated beverages and very acidic foods, which favor irritation.
Control of risk factors
Tobacco is one of the main enemies of the gums: it masks the symptoms and accelerates the progression of the disease. Reducing stress and getting plenty of rest also helps to keep the immune system in balance, favoring the body’s response to inflammation.
Additional measures
In people with a greater predisposition to periodontal disease, the dentist may recommend additional preventive treatments such as fluoride applications, specific mouthwashes, or mouth guards if bruxism is present.
Consequences of not treating swollen gums
Ignoring swollen gums may seem harmless at first, but in the medium and long term it has serious consequences for both the mouth and general health.
Progression to periodontitis
What starts as simple gingivitis can progress to periodontitis if left untreated. This involves destruction of the bone that supports the teeth and, over time, can lead to tooth loss.
Tooth loss
Advanced periodontitis causes tooth mobility and, in many cases, irreversible tooth loss. This situation affects not only chewing function, but also esthetics and patient confidence.
Digestive problems
Difficulty chewing due to pain or loss of teeth affects digestion. The food reaches the stomach less crushed, which can cause gastrointestinal discomfort.
Impact on quality of life
Chronic bad breath, frequent bleeding and constant sensitivity create social discomfort and affect self-esteem.
General health implications
There is increasing scientific evidence linking periodontitis to systemic diseases:
- Increased risk of complications in diabetic patients.
- Relationship with cardiovascular problems.
- Possible link with preterm delivery and low birth weight.
When to seek emergency care for swollen gums
Swollen gums usually improve with proper hygiene and professional treatment, but in some cases they become a dental emergency. Recognizing these signs early is key to avoiding serious complications.
Warning signs that require immediate attention
- Abundant or persistent bleeding, even without brushing.
- Intense pain that does not improve with common analgesics.
- Swelling that spreads to the face, neck or makes it difficult to open the mouth.
- Sudden tooth mobility or sensation of teeth shifting position.
- Constant and severe bad breath, which does not improve with daily hygiene.
What to do while waiting for the appointment
If the emergency occurs at night or on holidays, it is advisable to go to an on-call pharmacy to obtain analgesics and mouthwashes to temporarily control the pain and inflammation until you can visit the dentist.
Why not wait
Gingival inflammation can hide an active infection. If left untreated, it can spread to nearby tissues and even to the blood, increasing the risk of systemic complications. The earlier the intervention, the easier the treatment and the better the prognosis.
To conclude
Swollen gums are a symptom that should never be overlooked. Although in some cases they may seem like a minor nuisance, they are always a sign that something is wrong with your oral health. Often it is gingivitis, which can be easily resolved if acted upon in time; however, if ignored, it can evolve into periodontitis with irreversible consequences, such as tooth loss.
Home remedies – such as salt water rinses, gentle brushing or antiseptic mouthwashes – help to temporarily soothe inflammation, but are no substitute for professional assessment. Only the dentist can remove tartar build-up and design a treatment plan that is appropriate for each patient.
Prevention is, once again, the best tool: thorough daily hygiene, regular check-ups and the elimination of risk factors such as smoking or poor diet are the key to maintaining healthy gums.
The main message is clear: healthy gums are the foundation of a long-lasting smile. At any sign of inflammation, the safest thing to do is to act as soon as possible and rely on professional care to preserve the health of your mouth and your overall well-being.
| Topic | Key content |
|---|---|
| Introduction | Swollen gums are a frequent warning sign. They indicate a problem that should be addressed as soon as possible. We explain causes, temporary remedies and prevention. |
| Why do gums become inflamed? | Accumulation of plaque and tartar, gingivitis, hormonal changes, tobacco, medications, vitamin deficiency and systemic diseases. |
| Symptoms of inflamed gums |
Mild: redness, tenderness, occasional bleeding. Severe: spontaneous bleeding, receding gums, persistent bad breath, tooth mobility, swelling extending to face/neck. |
| Temporary remedies | Warm salt water rinses, gentle brushing with a soft brush, chlorhexidine mouthwashes in short intervals, common analgesics, avoidance of tobacco/alcohol and irritating foods. |
| Prevention | Complete daily hygiene (brushing, flossing, interdentals), periodic check-ups and professional cleanings, diet rich in vitamins C and D, avoidance of tobacco, additional personalized measures. |
| Consequences of not treating | Evolution to periodontitis, dental loss, digestive problems, bad breath and impact on self-esteem, relationship with systemic diseases (diabetes, cardiovascular, pregnancy). |
| When to seek emergency care | Heavy bleeding, severe pain, widespread swelling, sudden tooth mobility, severe bad breath. Requires immediate dental attention. |
| Conclusion | Inflamed gums should never be ignored. Home remedies only provide relief. The key is prevention, proper hygiene and professional dental check-up. |
 Whatsapp
Whatsapp


